Have you ever wondered if pulmonary rehabilitation can actually improve lung function? This article aims to address that very question. Many individuals with lung diseases or chronic respiratory conditions undergo pulmonary rehab as part of their treatment plan, but what exactly does it entail and does it truly have a positive impact on lung function? Join us as we explore the potential benefits of pulmonary rehab in improving overall lung health and quality of life. Whether you are considering pulmonary rehab for yourself or a loved one, understanding the potential outcomes can provide clarity and reassurance.
Overview of Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Definition of pulmonary rehabilitation
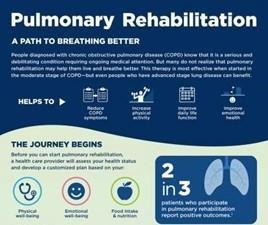
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a comprehensive program designed to improve the overall well-being and functioning of individuals with chronic lung diseases. It involves a multidisciplinary approach, combining exercise training, education, self-management strategies, and psychological support to enhance lung function and quality of life.
Goal of pulmonary rehabilitation
The primary goal of pulmonary rehabilitation is to improve the functional capacity of the lungs and reduce the symptoms associated with lung diseases. This includes enhancing respiratory muscle strength, endurance, and overall physical fitness. Additionally, pulmonary rehabilitation aims to educate patients about their condition, promote self-management strategies, and provide the necessary tools to lead a healthier lifestyle.
Components of pulmonary rehabilitation
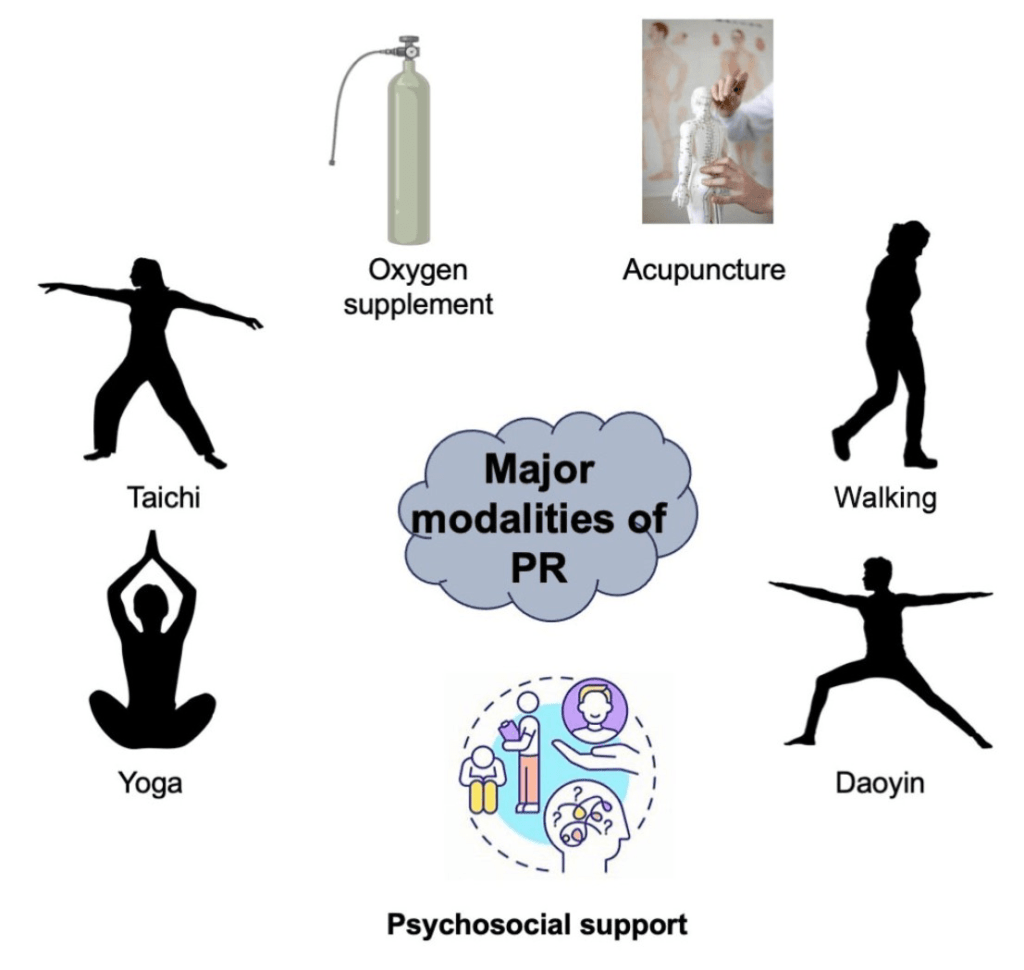
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs typically consist of several key components. These include exercise training, education and self-management, nutritional counseling, and psychological support. Each component is tailored to the individual needs of the patient and works together to maximize the benefits of pulmonary rehabilitation.
Understanding Lung Function
Overview of lung function
Lung function refers to the ability of the lungs to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. It involves various processes, including inhalation, gas exchange, and exhalation. Lung function is crucial for maintaining adequate oxygen levels in the body and removing waste products.
Factors affecting lung function
Several factors can influence lung function, including smoking, environmental pollutants, respiratory infections, and genetic predisposition. Chronic lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma, can also significantly impact lung function.
Measurement of lung function
Lung function is measured through various tests, such as spirometry, which measures the volume of air exhaled in a certain amount of time, and diffusion capacity, which assesses the ability of the lungs to transfer gas. These tests provide valuable insights into the overall functioning of the respiratory system and help guide treatment decisions.
Effects of Pulmonary Rehab on Lung Function
Studies examining the impact of pulmonary rehab on lung function
Numerous studies have investigated the effects of pulmonary rehabilitation on lung function in individuals with chronic lung diseases. These studies have consistently shown significant improvements in lung function parameters, including increased lung capacity, improved gas exchange, and enhanced respiratory muscle strength.
Positive findings of improved lung function
The positive findings of improved lung function in individuals who have undergone pulmonary rehabilitation are highly encouraging. Improvements in lung capacity can lead to better oxygenation of the body, increased exercise tolerance, and reduced breathlessness, ultimately enhancing overall quality of life.
Potential reasons for improvements
The exact mechanisms by which pulmonary rehabilitation improves lung function are not yet fully understood. However, several factors may contribute to these improvements. Regular exercise can enhance respiratory muscle strength and endurance, leading to improved lung capacity. Education and self-management strategies can also help individuals optimize their lung function by teaching them how to manage their symptoms more effectively.
Duration and intensity of pulmonary rehab
The duration and intensity of pulmonary rehabilitation programs can vary depending on individual needs and the specific lung condition being addressed. However, research suggests that longer programs with higher exercise intensity tend to yield more significant improvements in lung function. Regular attendance and adherence to the program are crucial for achieving optimal results.
Other Benefits of Pulmonary Rehab
Improved exercise capacity
In addition to enhancing lung function, pulmonary rehabilitation also improves exercise capacity. Regular exercise training helps individuals build strength, endurance, and cardiovascular fitness, enabling them to engage in physical activities with less fatigue and breathlessness.
Reduced breathlessness
Breathlessness, also known as dyspnea, is a common symptom experienced by individuals with chronic lung diseases. Pulmonary rehabilitation can help reduce breathlessness by improving lung function, enhancing respiratory muscle strength, and teaching individuals techniques to manage their symptoms better.
Improved quality of life
Living with a chronic lung disease can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Pulmonary rehabilitation aims to address not only the physical aspects of the condition but also the psychological and social impact. By improving lung function, reducing symptoms, and providing psychological support, pulmonary rehabilitation can greatly enhance an individual’s overall quality of life.
Reduced hospitalizations
By improving lung function and equipping patients with self-management strategies, pulmonary rehabilitation has been shown to reduce hospitalizations related to chronic lung diseases. This not only benefits the individuals by minimizing the risk of exacerbations but also contributes to cost savings for healthcare systems.

Factors Influencing the Effectiveness of Pulmonary Rehab
Patient selection
Proper patient selection is crucial for the effectiveness of pulmonary rehabilitation programs. It is essential to consider factors such as disease severity, comorbidities, and the patient’s ability and motivation to participate fully in the program.
Compliance and adherence to the program
The success of pulmonary rehabilitation heavily relies on the patient’s compliance and adherence to the program. Regular attendance, active engagement in exercise training, and implementation of self-management strategies are vital for achieving optimal results.
Individual variability
Each individual responds differently to pulmonary rehabilitation. Factors such as age, overall health status, and disease progression can influence the effectiveness of the program. Tailoring the program to the individual’s specific needs and monitoring their progress closely can help optimize outcomes.
Co-existing medical conditions
The presence of co-existing medical conditions can impact the effectiveness of pulmonary rehabilitation. It is important to consider these conditions when developing and implementing the program to ensure comprehensive and holistic care for the individual.
Appropriate Candidates for Pulmonary Rehab
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients are prime candidates for pulmonary rehabilitation. COPD is a progressive lung disease characterized by airflow limitation, and pulmonary rehabilitation has been shown to significantly improve lung function, exercise capacity, and quality of life in this population.
Asthma patients
While asthma is primarily characterized by airway inflammation and bronchospasm, individuals with asthma can also benefit from pulmonary rehabilitation. Asthma patients who experience impaired lung function, reduced exercise tolerance, or frequent exacerbations may find significant improvements through pulmonary rehabilitation interventions.
Interstitial lung disease patients
Interstitial lung diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis, can severely impact lung function and overall well-being. Pulmonary rehabilitation programs tailored to the specific needs of interstitial lung disease patients can help improve symptoms, functional capacity, and quality of life.
Lung transplant patients
Individuals who have undergone lung transplantation often require specialized care to optimize their lung function and overall recovery. Pulmonary rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation process, helping transplant recipients regain strength, improve lung function, and adapt to their new respiratory system.

Components of a Pulmonary Rehab Program
Exercise training
Exercise training is a cornerstone of pulmonary rehabilitation. It typically includes aerobic exercises, resistance training, and flexibility exercises. Regular physical activity helps improve lung function, build muscle strength, enhance cardiovascular fitness, and increase overall endurance.
Education and self-management
Education and self-management strategies are essential components of pulmonary rehabilitation. By providing individuals with a better understanding of their condition, teaching them appropriate coping mechanisms, and equipping them with tools for self-management, patients can take an active role in managing their lung health.
Nutritional counseling
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in supporting overall health and lung function. Nutritional counseling in pulmonary rehabilitation programs helps patients understand the importance of a balanced diet, maintain a healthy weight, and make informed food choices that positively impact their lung health.
Psychological support
Dealing with a chronic lung disease can be emotionally challenging. Pulmonary rehabilitation programs incorporate psychological support to address the mental and emotional well-being of patients. This may involve counseling, stress management techniques, and support groups to help individuals cope with the psychological impact of their condition.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Pulmonary Rehab
Lung function tests
To assess the effectiveness of pulmonary rehabilitation programs, various lung function tests are conducted. These tests, such as spirometry, diffusion capacity, and lung imaging, provide objective measurements of lung function and track changes over time.
Exercise tolerance tests
Exercise tolerance tests, such as the six-minute walk test or cardiopulmonary exercise testing, assess an individual’s ability to perform physical activities and measure their exercise capacity. These tests provide valuable information about improvements in endurance, cardiovascular fitness, and overall exercise tolerance.
Quality of life assessments
Quality of life assessments are an important aspect of measuring the effectiveness of pulmonary rehabilitation. These assessments capture a patient’s subjective experience of their physical, psychological, and social well-being, allowing healthcare providers to evaluate the impact of the program on the individual’s overall quality of life.
Patient-reported outcomes
Patient-reported outcome measures, such as questionnaires and surveys, provide valuable insights into the patient’s perspective on the effectiveness of pulmonary rehabilitation. These measures capture information about symptom severity, functional limitations, and the individual’s perception of their own health.

Combination Therapy for Optimal Results
Pharmacological interventions
Pharmacological interventions, such as bronchodilators, anti-inflammatory medications, and oxygen therapy, may complement pulmonary rehabilitation to further optimize lung function and symptom management. These treatments, when used in conjunction with pulmonary rehabilitation, can provide a more comprehensive approach to care.
Oxygen therapy
For individuals with severe lung disease, supplemental oxygen therapy may be necessary. Oxygen therapy can improve oxygenation, reduce breathlessness, and enhance exercise capacity. When incorporated into the pulmonary rehabilitation program, oxygen therapy can amplify the benefits of rehabilitation exercises.
Surgical interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions, such as lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplantation, may be necessary to improve lung function and overall quality of life. Pulmonary rehabilitation is often an integral part of the pre- and post-operative care for individuals undergoing these procedures, ensuring optimal recovery and rehabilitation.
Additional therapies
Additional therapies, such as respiratory muscle training, airway clearance techniques, and relaxation techniques, may also be incorporated into pulmonary rehabilitation programs to address specific needs and enhance outcomes. These therapies help target specific aspects of lung function and support overall respiratory health.
Conclusion
Summary of findings
In summary, pulmonary rehabilitation is a highly effective program that aims to improve lung function, exercise capacity, and overall quality of life for individuals with chronic lung diseases. This comprehensive approach, combining exercise training, education, self-management strategies, and psychological support, has been shown to yield significant improvements in lung function parameters and reduce symptoms associated with lung diseases.
Importance of pulmonary rehab
The importance of pulmonary rehabilitation cannot be overstated. By addressing the physical, psychological, and social aspects of chronic lung diseases, pulmonary rehabilitation helps individuals regain control over their health and live fulfilling lives. It empowers patients with the knowledge and skills to manage their condition effectively, reducing hospitalizations and improving their overall well-being.
Directions for further research
While numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of pulmonary rehabilitation, further research is needed to refine and optimize the program. Future studies could explore the long-term effects of pulmonary rehabilitation, investigate the ideal duration and intensity of the program, and identify the most effective interventions for specific patient populations. Additionally, research could focus on ways to enhance patient adherence and explore innovative approaches, such as telemedicine, to increase access to pulmonary rehabilitation programs.