Are you curious to learn more about respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and its impact on young children? RSV is a common respiratory virus that affects the lungs and airways. In this article, we will explore the key facts about RSV, including its symptoms, transmission, and potential complications. By understanding the basics of RSV, you can better protect the health and well-being of your little ones. So, let’s dive into the world of RSV and arm ourselves with the knowledge necessary to keep our children safe and healthy.

What is Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)?
Definition and Overview
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common respiratory virus that primarily affects young children. It is a leading cause of bronchiolitis (inflammation of the small airways in the lungs) and pneumonia in infants and children under the age of 1. RSV can also affect older children, adults, and the elderly, but the symptoms are generally milder. In severe cases, RSV can lead to hospitalization, especially in babies born prematurely or with underlying health conditions.
Transmission and Spread
RSV is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The virus can survive on surfaces for several hours, making it easy to contract by touching contaminated objects and then touching your face. RSV is most prevalent during the winter and early spring months, leading to outbreaks in schools, daycare centers, and other crowded places.
Seasonality
RSV exhibits a seasonal pattern, with outbreaks occurring primarily during the colder months. In temperate climates, such as the United States, RSV season typically begins in November and lasts through April. However, the timing and severity of the season may vary from year to year and across different regions. Understanding the seasonality of RSV helps healthcare providers and public health officials prepare for increased cases and implement appropriate preventive measures.
Signs and Symptoms of RSV Infection
Common Symptoms
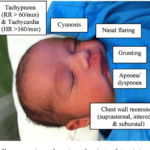
RSV typically starts with symptoms similar to the common cold, including a runny or stuffy nose, cough, mild fever, and sore throat. These symptoms usually appear 4-6 days after exposure to the virus. In infants and young children, RSV can also cause irritability, decreased appetite, and difficulty breathing. The severity of symptoms can vary from mild to severe, with some children experiencing significant respiratory distress and requiring medical intervention.
Severity and Complications
In most cases, RSV infection causes mild to moderate symptoms and resolves within one to two weeks. However, some children, particularly those at high risk, may develop severe lower respiratory tract infections such as bronchiolitis or pneumonia. These complications can lead to difficulty breathing, wheezing, and even respiratory failure. Prompt medical attention is crucial for children exhibiting severe symptoms or respiratory distress.
Difference from Common Cold
While the initial symptoms of RSV may resemble those of a common cold, there are key differences. Unlike a cold, RSV tends to cause more severe lower respiratory symptoms, such as wheezing and rapid breathing. Young infants, especially those born prematurely, are more susceptible to severe RSV infections than older children. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if your child’s symptoms worsen or if they are having difficulty breathing.
Diagnosing RSV in Young Children
Medical Evaluation
When a child presents with symptoms suggestive of RSV infection, a healthcare provider will conduct a thorough medical evaluation. This typically includes obtaining a detailed medical history, assessing vital signs, and performing a physical examination. The healthcare provider will pay close attention to the child’s breathing pattern, lung sounds, and signs of respiratory distress.
Laboratory Tests
To confirm an RSV infection, a healthcare provider may collect a respiratory sample, typically obtained through a nasal or throat swab. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for testing. Laboratory tests, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), can detect the genetic material of the RSV virus and provide a definitive diagnosis. These tests are especially valuable for high-risk populations and severe cases.
Differential Diagnosis
Distinguishing RSV from other respiratory illnesses, such as influenza or adenovirus, can be challenging based on symptoms alone. Laboratory testing is crucial to accurately diagnose RSV and guide appropriate management. Additionally, healthcare providers may consider the child’s medical history, clinical presentation, and the prevalence of RSV in the community when making a differential diagnosis.
Treatment and Management of RSV Infection
Supportive Care
In most cases, RSV infection is managed through supportive care. This involves ensuring adequate hydration, providing fever-reducing medications (if necessary and as directed by a healthcare provider), and using humidifiers to ease breathing. Over-the-counter cold medications are generally not recommended for young children and should only be used under a healthcare professional’s guidance. It is important to monitor the child closely and seek medical attention if symptoms worsen or if there are signs of respiratory distress.
Antiviral Medication
For certain high-risk populations or severe cases, antiviral medications may be prescribed to treat RSV. These medications, such as ribavirin, work by inhibiting viral replication and can help reduce the duration and severity of symptoms. Antiviral therapy is typically reserved for hospitalized patients or those with compromised immune systems. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate treatment plan for an RSV infection.
Hospitalization and Intensive Care
Severe RSV infections, particularly in high-risk individuals, may require hospitalization for close monitoring and supportive care. Hospitalization allows healthcare providers to closely observe the child’s breathing, administer oxygen if necessary, and provide additional respiratory support if needed. Intensive care may be required for infants with severe respiratory distress, requiring mechanical ventilation or other advanced interventions.

Prevention and Control Measures
Hygiene Practices
Practicing good hand hygiene is a crucial step in preventing the spread of RSV. Wash your hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after being in contact with someone who is ill or around potentially contaminated surfaces. Additionally, teach young children proper handwashing techniques and encourage them to cover their mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing. If soap and water are not available, use hand sanitizers with at least 60% alcohol content.
Vaccination
Currently, there is no vaccine available to prevent RSV infection. However, ongoing research and development efforts aim to develop an effective and safe vaccine. For high-risk populations, such as premature infants and children with chronic conditions, the healthcare provider may administer a preventive medication called palivizumab. This medication provides temporary immunity against RSV and reduces the risk of severe infection.
Isolation and Quarantine
If your child is diagnosed with RSV, it is important to take precautions to prevent the spread of the virus to others. Keep your child at home and limit contact with individuals who have weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions. Avoid crowded places, such as daycare centers, until your child has fully recovered and is no longer contagious. Follow the guidance of your healthcare provider regarding the duration of isolation and quarantine measures.
RSV in High-Risk Populations
Premature Babies
Premature babies are at higher risk of severe RSV infection due to their underdeveloped immune systems and immature lungs. Healthcare providers often recommend preventive measures, such as administering palivizumab during RSV season, to reduce the risk of severe illness in premature infants. It is crucial for parents and caregivers of premature babies to closely monitor for any signs of respiratory distress and seek immediate medical attention if necessary.
Children with Chronic Health Conditions
Children with chronic health conditions, such as congenital heart disease, asthma, or cystic fibrosis, are more susceptible to severe RSV infections. The virus can exacerbate underlying respiratory issues and lead to complications. Healthcare providers may recommend preventive measures, such as palivizumab administration, and closely monitor these children for any signs of RSV infection. Regular follow-up appointments and adherence to prescribed medications are essential for optimal management.
Elderly and Immunocompromised Individuals
Although RSV primarily affects young children, it can also cause severe illness in the elderly and individuals with compromised immune systems. These populations are more susceptible to infections and may experience more severe symptoms. Caregivers of elderly individuals and those with weakened immune systems should take extra precautions to prevent RSV transmission, such as practicing good hand hygiene and avoiding close contact with individuals who may be sick.

Long-Term Effects and Complications
Respiratory Problems
RSV infections, particularly severe cases, can have long-term effects on respiratory health. Some individuals, especially those with a history of severe RSV infection in early childhood, may experience recurrent wheezing and develop asthma later in life. It is important to monitor respiratory health and seek appropriate medical care if any respiratory problems arise.
Asthma Development
RSV infection is considered one of the leading risk factors for asthma development in children. While not all children who contract RSV will develop asthma, it is important to be vigilant for any signs of wheezing or persistent respiratory symptoms. Early intervention and regular follow-up with healthcare providers can help minimize the risk and manage symptoms effectively.
Related Health Issues
Severe RSV infections can be associated with an increased risk of other respiratory illnesses, such as pneumonia and bronchitis. Additionally, the stress and strain on the body caused by RSV can lead to secondary bacterial infections. Continuous monitoring of symptoms and prompt medical attention are essential to identify and treat any related health issues.
Research and Development
Vaccine Development
Efforts are underway to develop an RSV vaccine to prevent severe infections and reduce the overall burden of the virus. Researchers are exploring different vaccine strategies, including live attenuated vaccines, protein subunit vaccines, and viral vector-based vaccines. Vaccines that provide both short-term and long-term immunity are being actively pursued to protect vulnerable populations, including young children and older adults.
Antiviral Therapies
Advancements in antiviral therapies for RSV are also being investigated. Scientists are studying novel compounds that target specific viral proteins and inhibit RSV replication. Additionally, research is focusing on developing more effective and accessible antiviral drugs for high-risk individuals. These therapies aim to reduce the duration and severity of RSV infections, ultimately improving outcomes for those affected.
Public Health Strategies
Public health officials and researchers are continually working to improve RSV surveillance, prevention, and control strategies. Enhanced surveillance systems help monitor the circulation and genetic diversity of RSV strains, allowing for better preparedness and more targeted interventions. Educating healthcare providers, caregivers, and the general public about RSV and its prevention remains a crucial aspect of these strategies.
RSV Awareness and Education
Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns play a vital role in increasing awareness about RSV and promoting preventive measures. These campaigns often target parents, caregivers, healthcare professionals, and educators to ensure that accurate information about RSV is disseminated. By raising awareness, public health campaigns help reduce the impact of RSV infections, prevent severe cases, and promote timely medical intervention.
Information Resources
Various sources provide reliable information about RSV, including government health agencies, reputable medical websites, and healthcare provider organizations. These resources offer guidance on RSV prevention, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. It is essential to rely on reputable sources, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or the World Health Organization (WHO), for accurate and up-to-date information.
Advice for Parents and Caregivers
Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in preventing RSV infections in young children. It is important to practice good hand hygiene, limit exposure to sick individuals, and ensure that infants have a clean and safe environment. If your child exhibits symptoms suggestive of RSV, seek prompt medical attention. Follow the advice of healthcare professionals regarding the management of symptoms, preventive measures, and when to seek emergency care.
Future Outlook for RSV Prevention and Control
Advancements in Science and Medicine
Ongoing advancements in science and medicine hold promise for the prevention and control of RSV. The development of an effective vaccine and more targeted antiviral therapies can significantly reduce the burden of RSV infections, particularly in high-risk populations. Continued research and innovation are essential to translate these advancements into effective interventions.
Collaborative Efforts
Addressing the challenges posed by RSV requires collaborative efforts among researchers, public health officials, healthcare providers, and policymakers. Sharing knowledge, expertise, and resources is critical in developing comprehensive strategies for RSV prevention, diagnosis, and management. Collaborations at the local, national, and international levels can accelerate progress and help ensure that effective interventions are accessible to all.
Challenges and Opportunities
While significant progress has been made in understanding and managing RSV, challenges remain. Developing a safe and effective vaccine, particularly for vulnerable populations like premature infants, presents unique challenges. Additionally, ensuring equitable access to preventive measures and diagnostic tools is crucial for reducing the impact of RSV globally. Addressing these challenges and capitalizing on emerging opportunities will be essential in preventing and controlling RSV infections in the future.
In conclusion, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a common respiratory virus that primarily affects young children. Understanding the definition, transmission, and seasonality of RSV is crucial in preventing its spread. Recognizing the signs and symptoms, diagnosing RSV through medical evaluation and laboratory tests, and managing the infection with supportive care or antiviral medications are essential for optimal outcomes. Preventive measures, such as practicing good hygiene, vaccination, and isolation when necessary, play a key role in controlling RSV transmission. High-risk populations, including premature babies, children with chronic health conditions, and elderly individuals, require special attention and preventive measures. Long-term effects and complications of RSV can impact respiratory health and increase the risk of asthma development. Ongoing research and development efforts, along with public health campaigns, are essential in raising awareness, providing reliable information, and promoting preventive measures. Collaborative efforts, advancements in science and medicine, and addressing challenges and opportunities are necessary for the future prevention and control of RSV.