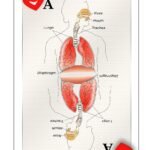
Living with COPD can be challenging, but understanding the potential journey ahead can help ease some of the uncertainty and provide a sense of direction. In this article, we will explore the life expectancy of a person with COPD. From discussing the factors that influence it to the steps you can take to maximize your quality of life, we aim to empower you with the knowledge you need to navigate your COPD journey with confidence. So, let’s embark on this informative adventure together!
Factors Affecting Life Expectancy
Age
Age is a significant factor that affects life expectancy in individuals with COPD. As you grow older, your lungs naturally become less efficient, making it harder to breathe. This decline in lung function is further exacerbated by the presence of COPD, leading to a higher risk of complications and a shorter life expectancy.
Smoking
Smoking is the leading cause of COPD, and it has a detrimental impact on life expectancy. If you smoke, it is essential to quit as soon as possible to slow down the progression of the disease and improve your chances of a longer life. Quitting smoking not only benefits your lung health but also reduces the risk of other smoking-related diseases such as heart disease and lung cancer.
Disease Severity
The severity of COPD is another crucial factor that influences life expectancy. Individuals with milder forms of the disease generally have a better prognosis and longer life expectancy compared to those with more advanced stages. Early diagnosis and appropriate management can slow down disease progression and positively impact life expectancy.
Comorbidities
COPD often coexists with other health conditions, known as comorbidities. Conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and lung cancer can further complicate the management of COPD and negatively impact life expectancy. It is essential to manage these comorbidities effectively and collaboratively with your healthcare team to optimize outcomes and improve your overall health.
Treatment Compliance
Adherence to treatment plans and medication regimens is critical in managing COPD and improving life expectancy. Following your healthcare provider’s recommendations, taking prescribed medications as instructed, and attending regular check-ups are vital components of effective COPD management. By diligently following your treatment plan, you can reduce symptom severity, prevent complications, and potentially increase your life expectancy.
Average Life Expectancy
Global Average
The average life expectancy of individuals with COPD varies across different countries and regions. Factors such as access to healthcare, environmental conditions, and socioeconomic factors can influence this average. Globally, the average life expectancy for individuals with COPD ranges from about 63 to 80 years.
Severity-based Estimates
Life expectancy estimates based on the severity of COPD can provide a more targeted outlook for individuals at different stages of the disease. Generally, individuals with mild COPD have a better prognosis and can expect a longer life expectancy compared to those with more severe stages. However, it is important to remember that these estimates are based on population data and individual outcomes may vary.
Gender Differences
Gender can also play a role in life expectancy for individuals with COPD. Women, in general, have a higher life expectancy compared to men. However, studies have shown that men with COPD tend to experience more rapid declines in lung function and may have a lower life expectancy compared to women with the same severity of the disease. It is crucial for both men and women with COPD to receive appropriate care and support to optimize their outcomes.

Stages of COPD and Life Expectancy
Stage 1 – Mild
In the mild stage of COPD, individuals may experience mild symptoms such as occasional coughing and shortness of breath. Life expectancy at this stage can be relatively normal, especially with early diagnosis and effective management. By quitting smoking, engaging in regular physical activity, and following prescribed treatment plans, individuals with mild COPD can significantly improve their quality of life and potentially increase their life expectancy.
Stage 2 – Moderate
At the moderate stage of COPD, symptoms become more noticeable and may interfere with daily activities. Life expectancy at this stage is generally reduced compared to the mild stage. However, with appropriate management, including medication, pulmonary rehabilitation, and lifestyle changes, individuals can still maintain a good quality of life and slow down disease progression.
Stage 3 – Severe
The severe stage of COPD is characterized by worsening symptoms, frequent exacerbations, and limitations in physical activity. Life expectancy may be significantly reduced at this stage. However, personalized treatment plans, including supplemental oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, and advanced medications, can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Stage 4 – Very Severe
The very severe stage of COPD is the most advanced and is associated with severe airflow limitation and significant impairment of lung function. Individuals at this stage often experience frequent exacerbations, respiratory failure, and severely limited physical activity. Life expectancy is noticeably reduced compared to earlier stages. At this stage, palliative and end-of-life care become essential in providing comfort and support to individuals and their families.
Improving Life Expectancy
Quitting smoking
Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to improve life expectancy in individuals with COPD. By quitting smoking, you can slow down the progression of the disease, decrease the frequency and severity of symptoms, and reduce the risk of other smoking-related diseases. Utilize available resources like smoking cessation programs, support groups, and nicotine replacement therapies to help you successfully quit smoking.
Pulmonary rehabilitation
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a comprehensive program that combines exercise, education, and support to improve lung function and overall well-being in individuals with COPD. By participating in pulmonary rehabilitation, you can enhance your physical endurance, learn effective self-management techniques, and improve your quality of life. Regular attendance and adherence to the program can positively impact life expectancy.
Medication and Treatment Options
There are various medications and treatment options available to manage COPD symptoms and improve outcomes. Bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and other medications can help open up the airways, reduce inflammation, and alleviate symptoms. It is crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan and ensure proper medication use to optimize your health and potentially increase your life expectancy.
Preventive Measures
Preventive measures play a vital role in managing COPD and improving life expectancy. Avoiding respiratory irritants, such as secondhand smoke and air pollution, can help reduce the risk of exacerbations and slow down disease progression. Additionally, staying up to date with vaccinations, such as the flu and pneumonia vaccines, can prevent respiratory infections and their complications.

Prognosis and Survival Rates
Survival Rates
Survival rates in individuals with COPD can vary depending on several factors, including disease severity, comorbidities, and overall health status. It is important to note that survival rates are estimates based on population data and individual outcomes may differ. On average, the five-year survival rate for individuals with COPD ranges from 40% to 70%. With appropriate management and adherence to treatment plans, individuals can improve their chances of survival and potentially exceed these estimates.
Prognostic Factors
Prognostic factors are indicators that help predict the likely outcome or progression of a disease. In COPD, factors such as lung function, exercise capacity, exacerbation frequency, and comorbidities can influence prognosis. Your healthcare provider will assess these factors and develop a personalized prognosis based on your unique circumstances. Regular monitoring, proactive management, and open communication with your healthcare team can help optimize your prognosis.
COPD Exacerbations
Exacerbations, or flare-ups, of COPD can be serious and potentially life-threatening. They often result in hospitalizations and can significantly impact life expectancy. By managing underlying triggers, adhering to treatment plans, and promptly seeking medical attention at the first sign of exacerbations, you can minimize the frequency and severity of these episodes and improve your overall prognosis.
Quality of Life
Maintaining Independence
Maintaining independence and a good quality of life is a priority for individuals with COPD. By actively managing the disease, following treatment plans, and practicing self-care strategies, you can enhance your ability to perform daily activities, reduce symptom burden, and maintain your independence for longer periods of time. Seeking support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals can also help in this endeavor.
Managing Symptoms
COPD symptoms, such as coughing, breathlessness, and fatigue, can significantly impact daily life. Managing these symptoms effectively through medication, pulmonary rehabilitation, and lifestyle modifications is crucial in improving quality of life. By developing coping strategies, utilizing relaxation techniques, and pacing activities, you can better manage symptoms and maintain a higher level of functionality and well-being.
Psychological Support
Coping with COPD can take a toll on your mental and emotional well-being. Feelings of anxiety, depression, and stress are not uncommon. Seeking psychological support through counseling, support groups, or therapy can provide valuable tools and strategies to address these challenges. Understanding and addressing the emotional impact of COPD can positively impact your quality of life and overall outlook.
Palliative and End-of-life Care
In advanced stages of COPD, palliative and end-of-life care become important considerations. These forms of care focus on providing comfort, support, and symptom management to individuals nearing the end of their lives. Palliative care aims to enhance quality of life, while end-of-life care provides support to individuals and their loved ones during the terminal phase of the disease.

Early Warning Signs and Disease Monitoring
Recognizing Symptoms
Recognizing early warning signs and symptoms of exacerbations is crucial in managing COPD effectively. Common warning signs include increased difficulty in breathing, increased wheezing, changes in sputum color, and a decrease in exercise tolerance. By being vigilant and seeking medical attention promptly when these signs arise, you can prevent exacerbations and minimize their impact on your health.
Monitoring Lung Function
Regular monitoring of lung function through spirometry and other tests is an important component of COPD management. These tests can help assess the severity of the disease, monitor progression, and guide treatment decisions. By staying proactive with lung function monitoring and discussing the results with your healthcare provider, you can make informed decisions about your care and potentially improve your outcomes.
Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential in managing COPD and monitoring your overall health. These appointments allow for ongoing assessment and adjustment of your treatment plan, identification of potential complications or comorbidities, and guidance on lifestyle modifications. By maintaining a consistent relationship with your healthcare team and attending regular check-ups, you can optimize your COPD management and improve your quality of life.
Early Intervention
Early intervention is crucial in managing COPD and prolonging life expectancy. Prompt recognition of symptoms, early diagnosis, and initiation of appropriate treatment can prevent disease progression, minimize complications, and improve outcomes. If you experience respiratory symptoms, such as persistent cough, shortness of breath, or difficulty in breathing, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to receive timely intervention.
Support and Resources
Patient Support Groups
Patient support groups provide valuable emotional support, education, and resources for individuals with COPD and their families. These groups offer a platform for sharing experiences, coping strategies, and tips for managing the disease. Connecting with others who understand the challenges of living with COPD can provide a sense of community and empowerment.
Caregiver Support
Caring for someone with COPD can be physically and emotionally demanding. Caregiver support programs and resources can provide guidance, education, and respite for caregivers. Taking care of your own well-being as a caregiver is essential in ensuring you can provide the best possible care for your loved one with COPD.
Financial Assistance
COPD management can involve significant healthcare costs, including medications, treatments, and hospitalizations. Financial assistance programs, insurance coverage, and government aid can help alleviate the financial burden associated with COPD. Exploring available resources and seeking assistance can ensure that financial constraints do not hinder access to necessary care and support.
Educational Materials
Educational materials, such as brochures, websites, and informational videos, can provide valuable information about COPD, its management, and available resources. These materials can help individuals with COPD and their families gain a better understanding of the disease, make informed decisions about their care, and access additional support when needed. It is important to rely on reputable sources and consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
Coping with the Emotional Impact
Anxiety and Depression
Anxiety and depression are common emotional challenges faced by individuals with COPD. These conditions can significantly impact quality of life and overall well-being. Seeking professional help through counseling, therapy, or medications can provide effective strategies for managing anxiety and depression. It is also important to engage in activities that bring joy and promote mental well-being, such as hobbies, spending time with loved ones, and pursuing interests.
Seeking Professional Help
If you are experiencing significant emotional distress or feel overwhelmed by the impact of COPD, seeking professional help is essential. Mental health professionals, such as psychologists or psychiatrists, can provide specialized support and guidance. They can help develop coping strategies, provide tools for managing stress and anxiety, and address any underlying mental health conditions.
Supportive Relationships
Building and maintaining supportive relationships with friends, family, and healthcare professionals can significantly impact your ability to cope with the emotional impact of COPD. Sharing your feelings and concerns with trusted individuals can provide validation, understanding, and practical support. Lean on your support network for encouragement, empathy, and assistance in day-to-day tasks.
Self-care Strategies
Engaging in self-care activities can help reduce stress, enhance well-being, and improve coping mechanisms. These activities can vary from individual to individual and may include exercise, meditation, journaling, and engaging in hobbies or creative outlets. Taking care of your physical, emotional, and mental well-being is crucial in managing the emotional impact of COPD and maintaining a good quality of life.
Research and Future Advances
Current Studies
Ongoing research is continually expanding our knowledge and understanding of COPD. Current studies focus on areas such as new medications, advanced treatment options, and personalized medicine approaches. Participating in clinical trials and staying informed about the latest research developments can offer individuals with COPD opportunities to access innovative treatments and potentially improve outcomes.
Potential Therapies
Researchers are exploring various potential therapies to address the underlying mechanisms of COPD and improve outcomes. These therapies include novel medications, targeted approaches to inflammation, gene therapies, and stem cell therapies. While many of these therapies are still in the experimental stage, they hold promise for the future of COPD treatment and potentially prolonging life expectancy.
Genetics and Personalized Medicine
Understanding the genetic factors that contribute to COPD can help personalize treatment approaches and improve outcomes. Genetic testing and research in this field aim to identify specific genetic variations that influence disease susceptibility, prognosis, and response to medications. By tailoring treatment plans to an individual’s genetic profile, it may be possible to optimize therapies and potentially increase life expectancy.
Lung Transplantation
In cases of end-stage COPD, lung transplantation may be an option to improve life expectancy. Lung transplantation involves replacing one or both diseased lungs with healthy donor lungs. This procedure can significantly improve lung function and quality of life in carefully selected individuals. However, lung transplantation is a complex procedure with risks and limitations. Evaluation by a specialized transplant team is necessary to determine eligibility and discuss the potential benefits and risks.
In conclusion, several factors impact the life expectancy of individuals with COPD. Age, smoking status, disease severity, comorbidities, and treatment compliance all play important roles in determining outcomes. However, it is important to remember that these factors are not absolute predictors, and individual circumstances can significantly influence life expectancy. By implementing lifestyle changes, adhering to treatment plans, and seeking appropriate support and care, individuals with COPD can optimize their quality of life and potentially extend their life expectancy. Ongoing research and advancements in COPD management offer hope for improved outcomes and better quality of life in the future.