I bet you’ve wondered about how asthma management actually works, haven’t you? Well, today is your lucky day because we’re here to shed some light on this commonly misunderstood topic. Understanding asthma management is vital for individuals with this condition, and also for those around them in order to provide the most effective support. So, let’s dive into the intricacies of asthma management and explore the strategies and techniques that can help ensure a healthier life for those living with asthma.
Understanding Asthma
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects the airways in your lungs. When you have asthma, your airways become inflamed and tightened, making it difficult for air to flow in and out. Asthma can vary in severity from mild to severe and can be triggered by a variety of factors, such as allergies, exercise, and exposure to certain irritants.
Definition of Asthma
Asthma is characterized by recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and coughing. These symptoms may occur during specific times, or they may be persistent. It is crucial to understand that asthma is a chronic condition, which means that it cannot be cured, but it can be managed effectively with the right treatment and lifestyle changes.

Causes of Asthma
The exact cause of asthma remains unknown, but certain factors are believed to contribute to its development. These include genetic predisposition, exposure to environmental allergens (such as pollen, pet dander, dust mites), respiratory infections, and exposure to tobacco smoke during childhood. It’s important to note that everyone’s triggers may vary, so what causes asthma symptoms in one person may not affect another.
Symptoms of Asthma
Common signs of asthma include wheezing (a high-pitched whistling sound when breathing), coughing (especially at night or early in the morning), chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These symptoms may be mild and intermittent, or they can be severe and persistent, leading to asthma attacks.

Severe Symptoms and Asthma Attacks
During an asthma attack, the symptoms worsen significantly and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. Signs of a severe asthma attack include extreme difficulty breathing, rapid breathing, inability to speak in full sentences due to breathlessness, and bluish discoloration of the lips and face. It is crucial to seek immediate medical help if experiencing these symptoms.
Diagnosis of Asthma
Diagnosing asthma involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider. They will typically start by taking a detailed medical history and conducting a physical examination. The doctor may ask about family history of asthma or allergies, frequency and severity of symptoms, and any known triggers.
To assess lung function, lung function tests such as spirometry may be performed. This involves breathing into a device that measures how much air you can exhale and how quickly. This test can help determine how well your lungs are functioning and if there is any airflow obstruction indicative of asthma.
Allergy testing may also be recommended. Allergies often coexist with asthma, so identifying specific allergens that trigger your symptoms can be helpful in developing a targeted treatment plan.

Types of Asthma Medications
Asthma medications aim to alleviate symptoms, prevent asthma attacks, and manage the underlying inflammation in the airways. There are three main types of asthma medications:
Bronchodilators: These medications relax the muscles in the airways, opening them up and allowing for better airflow. Short-acting bronchodilators provide quick relief during an asthma attack, while long-acting bronchodilators are used for long-term control and prevention of symptoms.
Anti-inflammatory drugs: These medications reduce inflammation in the airways, helping to prevent asthma symptoms and attacks. They are typically taken regularly as part of a long-term treatment plan to manage asthma.
Combination medications: Some individuals may require a combination of bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory drugs to achieve optimal asthma control. Combination medications typically contain both types of medications in a single inhaler for convenience.
Inhaler Techniques
Proper inhaler technique is crucial for the effectiveness of asthma medications. Inhaled medications are delivered directly to the airways, targeting the inflammation and providing quick relief. Here are a few essential points to know about inhaler use:
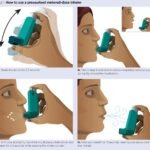
Importance of proper inhaler use: Using an inhaler correctly ensures that the medication reaches the lungs effectively and maximizes its benefits. When inhalers are not used properly, the medication may not be adequately delivered, leading to suboptimal asthma control.
Different types of inhalers: There are various types of inhalers available, including metered-dose inhalers (MDIs), dry powder inhalers (DPIs), and soft mist inhalers (SMIs). Each type has specific instructions for use, so it is essential to understand the correct technique for your specific inhaler.
Proper inhaler technique: Proper inhaler technique involves several steps, such as using a spacer if prescribed, shaking the inhaler, exhaling fully before inhalation, and coordinating the inhalation with the actuation of the inhaler. It is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider or pharmacist to ensure that you are using your inhaler correctly.
Asthma Action Plan
An asthma action plan is an individualized written document that outlines specific steps to manage asthma symptoms and prevent asthma attacks. By creating an asthma action plan, you and your healthcare provider can establish clear guidelines for your asthma management. Here are some key components of an asthma action plan:
Creating an individualized action plan: Your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a customized plan based on the severity of your asthma, your triggers, and your lifestyle. The plan will include steps to take when your symptoms worsen, as well as preventive measures.
Triggers and how to avoid them: Identifying triggers that worsen your asthma symptoms is crucial for effective management. Common triggers include allergens (such as pollen, mold, and dust), cold air, exercise, and certain medications. Your action plan will provide guidance on how to avoid or minimize exposure to these triggers.
Emergency measures: Your action plan should include instructions on what to do during an asthma attack or in an emergency situation. This may involve using rescue medications, when to seek medical help, and emergency contact information.
Environmental Control Measures
Taking steps to identify and reduce asthma triggers in your home can significantly improve asthma control. Some environmental control measures to consider include:
Identifying asthma triggers in the home: Common triggers in the home include dust mites, pet dander, mold, tobacco smoke, and strong odors. Conducting a thorough assessment of your living environment can help you identify and target these triggers.
Reducing or eliminating triggers: Once you have identified the triggers, taking steps to reduce or eliminate their presence in your home is crucial. This may involve using dust mite-proof covers on bedding, keeping pets out of bedrooms, fixing leaks and reducing humidity to prevent mold growth, and implementing a smoke-free policy.
Improving indoor air quality: Good indoor air quality is essential for asthma management. Regularly ventilating your home, using air purifiers, and maintaining clean living spaces can help reduce the presence of allergens and irritants in the air.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medication and environmental control measures, certain lifestyle changes can positively impact asthma management. Here are a few key lifestyle changes to consider:
Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can worsen asthma symptoms and make it more challenging to control the condition. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can improve lung function and overall asthma control.
Regular physical activity: Engaging in regular physical activity, within your abilities, can help improve lung capacity, strengthen respiratory muscles, and enhance overall fitness. It is important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate level of exercise for your specific needs and limitations.
Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke: Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke can trigger asthma symptoms and significantly worsen lung function. Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to smoke is essential for managing asthma effectively.
Monitoring Asthma Control
Regular monitoring of asthma control is crucial for evaluating treatment effectiveness and making any necessary adjustments. Here are some common methods of monitoring asthma control:
Peak flow monitoring: Peak flow meters are portable devices used to measure how well air is flowing out of your lungs. Regular peak flow monitoring can help identify changes in lung function and determine if your asthma is properly controlled.
Symptom diary: Keeping a record of your symptoms, triggers, and medication use can provide valuable insights into your asthma management. Recording any changes in symptoms or triggers can help you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about your treatment plan.
Regular check-ups with healthcare provider: Ongoing communication with your healthcare provider is essential to ensure that your asthma management plan is effective. Regular check-ups allow for adjustments in medication, evaluation of lung function, and addressing any concerns or questions you may have.
Managing Exacerbations
Even with proper asthma management, exacerbations (worsening of symptoms) can occur. Recognizing early warning signs and knowing how to respond is crucial. Here are some important points to manage exacerbations:
Recognizing early warning signs: Common early warning signs of an asthma exacerbation may include increased coughing, changes in mucus production, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Becoming familiar with your own early warning signs can help you take action before the symptoms escalate.
Using rescue medications: Rescue medications, such as short-acting bronchodilators, provide quick relief during an asthma exacerbation. It is important to have these medications readily available and know how to use them correctly in accordance with your asthma action plan.
Seeking medical help when necessary: If your symptoms do not improve with rescue medications or worsen rapidly, it is essential to seek medical help immediately. Delaying treatment during a severe asthma exacerbation can have serious consequences, and prompt medical intervention may be necessary.
In conclusion, understanding asthma and its management is crucial for effectively controlling this chronic respiratory condition. By working closely with your healthcare provider, following an individualized action plan, and making necessary lifestyle changes, you can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the impact of asthma on your daily activities. Remember to monitor your asthma control, seek immediate help during exacerbations, and never hesitate to ask questions or seek further guidance from your healthcare team. With proper management, asthma can be well-controlled, allowing you to live a healthy and active life.