If you have an elderly loved one or are a caregiver for an older adult, you may have wondered about the signs of respiratory distress in this age group. It’s important to be aware of these specific indicators as respiratory issues can be common and potentially serious in seniors. By recognizing the signs, you can take prompt action and ensure their well-being. In this article, we will explore the specific signs of respiratory distress to look out for in the elderly, providing you with valuable information to keep them safe and healthy.
Overview of Respiratory Distress
Respiratory distress refers to a condition in which an individual is experiencing difficulty breathing. This can occur in people of all ages, but it is particularly important to recognize the signs of respiratory distress in the elderly population. The ability to breathe properly is vital for maintaining overall health and well-being, and any impairment in respiratory function can lead to serious complications. By understanding the causes, signs, and symptoms of respiratory distress in the elderly, we can ensure prompt medical attention and take steps to prevent its occurrence.
Definition of Respiratory Distress
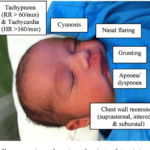
Respiratory distress is characterized by a range of symptoms that indicate an individual is having difficulty breathing. It may involve a variety of physical, behavioral, and emotional signs. Some common indicators of respiratory distress include rapid breathing, cyanosis (a bluish tint to the skin or lips), wheezing or crackling sounds in the chest, and the use of accessory muscles to aid in breathing. In addition, an individual experiencing respiratory distress may exhibit signs of restlessness, confusion, extreme fatigue, and difficulty speaking.
Causes of Respiratory Distress in the Elderly
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of respiratory distress in the elderly. Chronic respiratory conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and pneumonia can significantly impact an individual’s ability to breathe properly. Smoking history, heart conditions, and a weakened immune system also increase the risk of respiratory distress. Additionally, exposure to air pollution or respiratory irritants can aggravate respiratory symptoms and lead to distress.
Importance of Recognizing Respiratory Distress in the Elderly
Identifying respiratory distress in the elderly is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, prompt recognition allows for early intervention and appropriate medical treatment, which can improve outcomes and prevent further complications. Respiratory distress can be life-threatening if not addressed promptly, and the elderly population is particularly vulnerable to its effects. By recognizing the signs and symptoms, healthcare providers, caregivers, and family members can take the necessary steps to ensure the well-being and safety of their loved ones.
Physical Signs of Respiratory Distress
There are several physical signs that may indicate respiratory distress in the elderly. One such sign is cyanosis, which is characterized by a bluish discoloration of the skin or lips. This occurs when there is a lack of oxygen in the blood and is often a clear indicator that assistance is needed. Rapid breathing, also known as tachypnea, is another common physical sign. Wheezing or crackling sounds in the chest may also be present, indicating underlying respiratory issues. In severe cases, individuals may use accessory muscles, such as those in the neck and shoulders, to aid in breathing. Nasal flaring, where the nostrils widen with each breath, is another physical sign of respiratory distress to be mindful of in the elderly.
Behavioral Signs of Respiratory Distress
In addition to physical signs, there are several behavioral indicators that may suggest an elderly individual is experiencing respiratory distress. Restlessness or agitation may be observed, as the individual struggles to find a comfortable position or obtain sufficient oxygen. Confusion or altered mental status can also occur due to the decreased oxygen supply to the brain. Extreme fatigue or drowsiness may be present, as the effort required to breathe takes a toll on the body. Another behavioral sign is difficulty speaking or limited speech. This may be due to the individual’s focus on breathing or a weakened respiratory system impacting the vocal cords.
Emotional Signs of Respiratory Distress
Respiratory distress can also have emotional manifestations, particularly in the elderly. Anxiety or fear may arise as individuals struggle to catch their breath or feel a sense of suffocation. Panic may set in if they perceive an inability to breathe adequately. Furthermore, the prolonged nature of respiratory distress can lead to depression or withdrawal. The inability to engage in regular activities due to breathing difficulties can contribute to a sense of isolation and loss of enjoyment in life. Recognizing these emotional signs is crucial for providing appropriate support and intervention.
Additional Signs and Symptoms
In addition to the physical, behavioral, and emotional signs already mentioned, there are several other indicators of respiratory distress in the elderly. Coughing is a common symptom and may be accompanied by the production of mucus or phlegm. Chest pain or tightness can also occur, often due to the strain placed on the respiratory muscles. Shortness of breath, or dyspnea, is a significant symptom that may be experienced even during minimal exertion. Reduced exercise tolerance, where an individual becomes easily fatigued during physical activity, can also indicate respiratory distress. Lastly, a decrease in appetite or unexplained weight loss may be present, signaling the body’s increased energy expenditure and reduced ability to obtain nutrients due to respiratory difficulties.
Factors Increasing Risk of Respiratory Distress
Several factors increase the risk of respiratory distress in the elderly. Chronic respiratory conditions, such as COPD, asthma, or pneumonia, can significantly impair lung function and contribute to distress. Smoking history is another important risk factor, as it damages the respiratory system and weakens lung capacity. Heart conditions, such as congestive heart failure, can also lead to fluid accumulation in the lungs and subsequent respiratory distress. A weakened immune system puts elderly individuals at a greater risk of developing respiratory infections, further exacerbating respiratory symptoms. Additionally, exposure to air pollution or respiratory irritants, both indoors and outdoors, can worsen respiratory distress in susceptible individuals.
Importance of Prompt Medical Attention
Seeking prompt medical attention when respiratory distress is suspected is of utmost importance. Early intervention improves outcomes by allowing healthcare providers to address the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment. Respiratory distress can quickly escalate and become life-threatening if left untreated. By accessing medical care promptly, individuals can receive the necessary support and interventions to stabilize their breathing and prevent further complications. Timely medical attention is vital in safeguarding the health and well-being of elderly individuals experiencing respiratory distress.
Treatment options and prevention strategies
The treatment options for respiratory distress in the elderly may vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. A healthcare provider will conduct a thorough assessment and may prescribe medications to alleviate symptoms or manage chronic respiratory conditions. Oxygen therapy may also be administered to ensure an adequate oxygen supply. In some cases, respiratory support through mechanical ventilation may be necessary. Prevention strategies play a vital role in reducing the risk of respiratory distress in the elderly. Regular medical check-ups can help identify potential respiratory issues early on and allow for timely intervention. Vaccinations, such as the flu and pneumonia vaccines, are essential in protecting against respiratory infections. Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke is crucial, as exposure to tobacco smoke significantly impacts respiratory health. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can support overall respiratory function. Lastly, ensuring a clean and dust-free living environment can minimize exposure to respiratory irritants such as pet dander and dust mites.
Steps for Responding to Respiratory Distress
If you encounter an elderly individual experiencing respiratory distress, it is important to respond calmly and confidently. Your soothing presence and reassurance can help alleviate anxiety and create a sense of safety. The first step is to call emergency services immediately. They are equipped to handle respiratory emergencies and can provide the necessary medical care. If the individual has prescribed medications, administer them as instructed or as guided by emergency services. If applicable, assist with breathing techniques, such as pursed-lip breathing or diaphragmatic breathing, in a calm and supportive manner. It is essential to remember that staying calm and getting appropriate medical assistance are key to effectively responding to respiratory distress.
Preventing Respiratory Distress in the Elderly
Prevention is always better than cure, and there are several measures that can be taken to reduce the risk of respiratory distress in the elderly. Regular medical check-ups are crucial in monitoring respiratory health and identifying potential issues early on. Vaccinations against the flu and pneumonia are highly recommended to prevent respiratory infections, which can exacerbate distress. Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke is paramount, as tobacco smoke is a major contributor to respiratory issues. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and proper hydration, supports overall respiratory function. Lastly, ensuring a clean and dust-free living environment can minimize exposure to respiratory irritants and reduce the risk of respiratory distress.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of respiratory distress in the elderly is vital for early intervention and improved outcomes. By understanding the physical, behavioral, and emotional signs of distress, we can promptly seek medical attention and provide appropriate support to alleviate symptoms. Close monitoring and prevention strategies, such as regular medical check-ups, vaccinations, and avoiding respiratory irritants, can help reduce the risk of respiratory distress in the elderly. By prioritizing respiratory health in this vulnerable population, we can ensure their well-being and enhance their quality of life.